Producer Price Differentials (PPDs) are complicated and confusing. They also have a major impact on milk payments to producers. The prior two posts covered the negative PPDs in California and the five reasons for negative PPDs. One of the difficulties in understanding fluctuations and negative PPDs is that there are five factors at work all moving in different directions at different times. Based on comments from the post on the five reasons for negative PPDs, the explanations for two were difficult to understand and will be further explained in this post. They are the following:
- A significant amount of Class III is being de-pooled. That increases the amount of a negative PPD and lowers a positive PPD. When Class IV is de-pooled, it lowers a positive PPD.
- As less fluid milk is consumed, there is a smaller percentage of Class I milk in the mix. Because Class I pricing is formulated to be the highest paid milk, when there is a smaller percentage, the "Uniform" or average price will be lower.
Class I milk cannot be de-pooled and Class II milk is small enough to be inconsequential. Therefore, the de-pooling examples deal only with de-pooling of Class III and Class IV milk.
The Class III milk price paid to a producer is based on the value of milk protein, butterfat, and Other Solids in the delivered milk. That is the basis for the initial payment to producers in a Class and Component Federal Order. At the end of a month when the receipts are complete, a weighted average of the four Classes at their specific pricing formulas is calculated. This is known as the Uniform price. The PPD is the difference between the Uniform price and the initial payment based on components.
To better explain the reasons for the two events listed above that can lower a negative PPD, examples have been prepared below. In these examples, only one variable is changed at a time. All other variables are held constant to better understand the impact of each event. In the examples below Class III milk is de-pooled when it is high, and Class IV is de-pooled when it is high. Milk is de-pooled to avoid paying a negative PPD.
DE-POOLING WHEN CLASS III PRICE IS HIGHER THAN THE UNIFORM PRICE
Table I below shows the base case. In this example The Class III price is lower than the Uniform price causing a negative PPD. This happens when the Class IV milk is significantly lower than the Class III.
 |
| Table I - Negative PPD for base case |
Table II shows what happens as all the Class III milk in this example is de-pooled. The negative PPD doubles, going from -$.31 to -$.60 per cwt. While the Class III milk that was de-pooled has avoided the negative PPD, the balance is made up by those that are still in the pool.
 |
| Table II - Impact of de-pooling Class III milk |
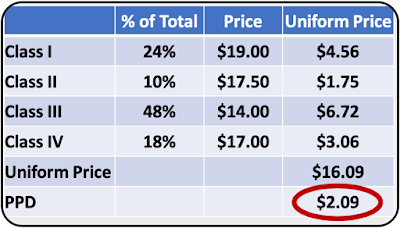 |
| Table IV - Class IV milk is priced above Class III milk |
 |
| Table V - Impact of de-pooling Class IV milk |
SUMMARY
Everything about the PPD is both complicated and confusing, but it is also very impactful on producer pricing. The chances of a high positive PPD are slim under the existing conditions. The short-term issue is the significantly lower price of Class IV milk compared to Class III milk. This is not likely to change in the short-term.



No comments:
Post a Comment